Examining donations ahead of European elections
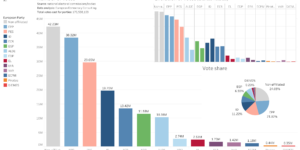
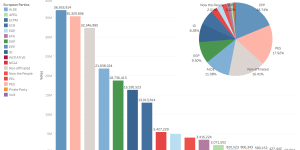
European Democracy Consulting’s analysis of donations to European political parties and foundations reveals crucial funding insights. During the six months leading up to the 2024 European elections, 20 entities received less than €422,000 combined. Private companies were the main donors, and the right-leaning parties secured 86% of donations. Recommendations include improving transparency and the format of reporting.